
| Name | Testosterone Propionate |
|---|---|
| CAS NO | 57-85-2 |
| EINECS | 200-351-1 |
| Molecular Formula | C22H32O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 344.4877 |
| Other Name | 17beta-(Propionyloxy)androst-4-en-3-one 17beta-Hydroxy-4-androsten-3-one 17-propionate Androlon Androst-4-en-3-one, 17beta-hydroxy-, propionate Androsteston Enarmon-oil Homandren Masenatel Testolets Testosterone-17-beta-propionate |
| Density | 1.1g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 118℃ |
| Boiling Point | 454.6°C at 760 mmHg |
| Refractive Index | 1.56 |
| Flash Point | 196.3°C |
| Water Solubility | <0.1 g/100 mL at 24.5℃ |
| Vapour Pressure | 1.89E-08mmHg at 25°C |
| Safety Information | |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | T |
| Risk Statements | 45-22-63 |
| Safety Statements | 53-36/37-45 |
| RIDADR | 2811 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | XA3115000 |
| HS Code | 29372900 |
| Toxicity | LD50 oral in rat: 1gm/kg |
| Testosterone propionate Usage And Synthesis | |
|---|---|
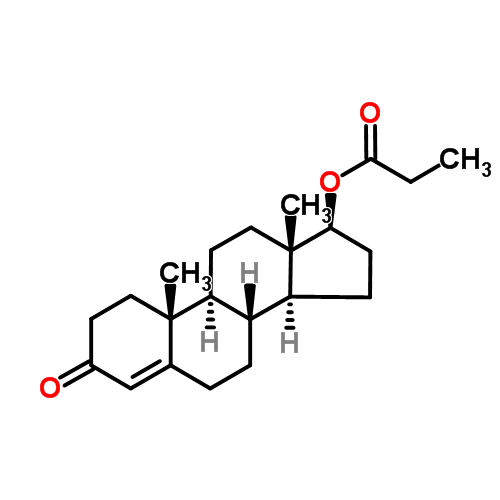
| Overview | Testosterone propionate, sold under the brand name Testoviron among others, is an androgen and anabolic steroid(AAS) medication that is used mainly in the treatment of low testosterone levels in men. Anabolic androgenic steroids(AAS) were originally developed in the late 1930s and used since 1950s to improve athletic performance, male physical attractiveness and improves body image for both sexes[1]. Athletes use AAS to increase strength, lean body mass, and, in some cases, improve physical appearance[2]. Accordingly, AAS increase body weight, fat-free mass, muscle size and strength training in healthy men receiving 600 mg of testosterone weekly for 10 weeks[3-5]. In the absence of strength training the muscle size is increased by higher doses of AAS[3,4] Figure 1 the chemical structure of testosterone propionate; |
| Applications | Testosterone propionate is often used for muscle mass building. The original medical indication is for the treatment of androgen deficiency in male adults either in hypogonadism or andropaus[7]. Nowadays testosterone propionate is indicated for its use in heifers in order to stimulate maximal growth[6]. Hypogonadism(the late puberty and premature termination of adolescent growth, some types of impotence) is the most common indication for AAS therapy in men. At present, The United States Food and Drug Administration(FDA) approved clinical use of AAS for treatment of hypogonadism, anemia accompanying renal and bone marrow failure, endometriosis, cancer and wasting syndrome in human immunodeficiency virus infection[8,9]. The other clinical uses of AAS include treatment of catabolic states and cachexia (i.e chronic obstructive pulmonary disease), corticosteroid therapy, osteoporosis, growth stimulation in male puberty, prophylaxis for hereditary angioedema, hepatic disease, and female to male transsexualism, hypoplastic anemia, multiple sclerosis, sexual dysfunction and depression. Testosterone is also available in several different pharmaceutical formulations and is recommended for use in veterinary medicine to treat chronic wasting conditions and improve appetite and physical appearance. In addition, veterinary compounding pharmacies offer for sale numerous testosterone ester preparations in oil and testosterone suspension in aqueous vehicle[10-12]. |
| Pharmacodynamics | The administration of testosterone propionate can induce production of proteins related to male sexual development. On the other hand, testosterone itself present an estrogenic activity due to interaction with aromatase enzyme, thus the continuous administration of testosterone propionate may cause the elevation of plasma estrogen. Clinical trials showed as well, a decrease in plasma LH after testosterone propionate administration[13]. |
| Mode of action | Anabolic steroids are thought to exert their actions by several different mechanisms. These mechanisms include modulating androgen receptor expression as a consequence of[i] intracellular metabolism and by[ii] directly affecting the topology of the androgen receptor and thus subsequent interaction with co-activators and transcriptional activity. Other mechanisms include[iii] an anticatabolic effect by interfering with glucocorticoid receptor expression; and[iv] by non-genomic, as well as by genomic pathways, in the CNS resulting in behavioural changes. These mechanisms are discussed herein. Free testosterone[T] is transported into the cytoplasm of target tissue cells, further binding to the androgen receptor, or being reduced to 5alpha-dihydrotestosterone(DHT) by the cytoplasmic enzyme 5alpha-reductase. The binding areas are called hormone response elements(HREs), and influence transcriptional activity of certain genes, producing the androgen effects.[14-16] |
| The relation to obesity | Several studies have demonstrated an inverse relationship between indicators of obesity(body mass index, waist circumference, a reliable indicator of visceral obesity), and testosterone levels over all age groups[15-17]. Obesity contributes to onset of type II diabetes mellitus(T2DM), dyslipidemia, hypertension and, therefore, MetS. An inverse association between the severity of features of MetS, T2DM and plasma testosterone has been previously reported[18]. In one study, this association was independent of age and body mass index[19], underlining the complexity of the relationship between testosterone and obesity[20]. This became also apparent from another study that verified the prevalence of low testosterone levels in male T2DM patients, related to variations in BMI, waist circumference, neuropathy, triglycerides, CRP, glucose, insulin and HOMAIR, but no increase of silent myocardial ischemia or peripheral arterial disease was established[21]. This is supported by other studies linking low testosterone, cardiovascular risk and insulin resistance(for review[22]). Although age is associated with the prevalence of MetS, young men with features of the MetS exhibit reduced testosterone levels[23, 24] and testosterone treatment in these individuals positively affects weight reduction, with concomitant reduction in insulin resistance(IR). The exact pathophysiological mechanisms responsible for reduced testosterone levels in obesity remain under investigation[15], however, hyperinsulinemia is shown to suppress serum testosterone levels[25]. Testosterone levels are reduced in men with T2DM, with an inverse association between testosterone levels and glycosylated hemoglobin(HbA1c)[26] and this occurs independently of medications, such as statins[27]. In men with low plasma testosterone, the likelihood of T2DM is increased and several large prospective studies have shown that low T testosterone levels predict development of T2DM in men. Low levels of testosterone are associated with a decreased lean body mass, and relative muscle mass is inversely associated with insulin resistance and prediabetes[28]. |
| Adverse reactions and precaution | Testosterone propionate is a kind of AAS. The most common reversible side effect of AAS is cosmetic in nature. The orally used AAS may cause hepatotoxicity. However there is no report describing hepatotoxicity due to use of parenteral AAS preparations, which appear to damage heart muscles in long-term use[29]. There are several side effects of AAS use such as; headaches, gastrointestinal irritation, fluid retention in the extremities, diarrhea, stomach pains, oily skin. Additionally jaundice, menstrual abnormalities, hypertension and infections at injection site may be observed. Acne develops in both sexes at puberty during treatment with AAS due to secretion of the natural oil sebum and growth of sebaceous glands[30]. Males using high doses of AAS may have elevated circulating estrogen levels similar to women during a normal menstral cycle. This effect is result of aromatization of testosterone in part to estrogens. Therefore, gynecomastia and breast pain may be observed in men taking high doses of AAS[31]. Chronic adverse effects associated with AAS abuse include acne, urogenital problems, endocrine abnormalities, neuropsychiatric disorders, hepatic and cardiovascular diseases. Acne is common adverse effect of AAS use seen in almost 50% of the androgen uses. Acne fulminans and acne conglobata are the most common forms of acne associated with AAS[32]. Subjects using AAS should be warned that acne associated with AAS can get worse with vitamin B supplement[32]. Gynecomastia and suppression of spermatogenesis are frequent consequences of AAS use. High dose of AAS suppresses the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis due to negative feedback and, it may take weeks or months for the axis to recover. Consequently atrophy of the seminiferous tubules during this time may result in subfertility or infertility[33]. Furthermore, subjects may continue to encounter symptoms of hypogonadism[erectile dysfunction, low libido and low vitality] even after discontinuation of AAS until the axis recovers. Recent reports suggest that use of clomiphene citrate may hasten the recovery of gonadal axis[34]. |
| Chemical Properties | White or almost white powder or colourless crystals |
| Uses | Anabolic steroid. Androgen. Controlled substance |
| Uses | androgen, antineoplastic |
| Brand name | Andro heart injecta;Androfort;Androlan in oils;Cortrifosal;Durateston v;Encilcort;Galanrent;Gondrone;Gyno-terazol;Hermo m;Jeifer-old;Malogen in oil;Malotrone;Micro-sterandryl;Napionate;Orchisterone-p;Pantesin;Perandern;Pertesis;Sterotest;Sutanone;Tesrina;Testanderogen;Testenat;Testigrmon;Testilen;Testirene;Testoici;Testoidral;Testonate;Testopinate;Testo-retard;Testoviron (ampule);Testoviron-10/-25/-50;Testoviron-depot-50/-100;Testovis;Testron;Tostrina;Triomone;Vantostol-p;Viromon. |
| World Health Organization (WHO) | In 1982, low dosage preparations of testosterone propionate, a synthetic ester of the naturally-occurring androgen, testosterone, were prohibited in Bangladesh following their inadmissable promotion as anabolic agents for use in malnourished children. Higher dosage preparations of testosterone propionate remain available in many countries, including Bangladesh, for several highly specific but limited indications including hypogonadism and the palliative treatment of inoperable breast cancer. |
| General Description | Odorless white or yellowish-white crystals or a white or creamy-white crystalline powder. |
| Air & Water Reactions | Insoluble in water |
| Reactivity Profile | Testosterone propionate is sensitive to light. Incompatible with alkalis and oxidizing agents |
| Fire Hazard | Flash point data for Testosterone propionate are not available; however, Testosterone propionate is probably combustible |
| Safety Profile | with experimental neoplastigenic, tumorigenic, and teratogenic data. Moderately toxic by ingestion and wintraperitoneal routes. Human male reproductive effects by intramuscular and parenteral routes: changes in spermatogenesis, testes, epid~dpmis, and sperm duct. Human female reproductive effects by intramuscular and parenteral routes: menstrual cycle changes or disorders and effects on ferthty. Experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes. See also TESTOSTERONE |
| Purification Methods | Crystallise the propionate from aqueous EtOH, or Et2O/pet ether (m 121o), and it has max at 240nm (EtOH), and [ ] 20 +114o (c 1, CHCl3). Also purify it by HPLC. [Ercol & de Ruggieri J Am Chem Soc 75 650, 652 1953, polymorphism: Brandst.tter-Kuhnert & Kofler Mickokim Acta 847, 850 1959, Beilstein 8 IV 977.] |
FAQ
MOQ: 100 gram
Pack material: Plastic bag + Shockproof film + shockproof envelope + Cartons.
Shipment: By express to buyers’ door. 100% make sure delivery.
Payment: TT/ Western Union/BTC/ETV/VISA and so on, please contact by email.
Shipment time: Within three working days after payment. Usually need ten days to arrive buyers’ address. Resend if lost.


Boldenone, Oxymetholone, Drostanolone, Testosterone, Nandrolone, Trenbolone
Designed by HuishangMedia
Copyright © 2008-2022 J·S Biology Co.,LTD All Rights Reserved
Design by Huishang Media
Under CC: ultimatearm, Freepik, Nhor Phai, DinosoftLabs, Vitaly Gorbachev, Kiranshastry, Pixel perfect
If you have any questions or ask for a quote, please submit your information here and we will respond to you immediately.